An Introduction to Homer’s Odyssey
Homer’s Odyssey is one of the greatest works of Western literature, telling the epic story of the Greek hero Odysseus and his long journey home after the Trojan War. Written around 800 BCE, the Odyssey has captivated audiences for thousands of years with its powerful storytelling, vivid imagery, and complex characters. The Odyssey is a nostos, or a story of return, and asks can one come home again, especially after years of bloody war? In fact, an odyssey is now meant generally as a long journey home, much like Odysseus’ after the fall of Troy. The Odyssey attempts to remake order after the chaos of war.
Odysseus, a young man when Agamemnon and Menelaus recruited him for the campaign against Ilium, is now a middle-aged survivor and veteran of that war who must be smarter than the champion Achilles and the leader Agamemnon in order to return home and set his lands in order. War almost seems easy in the light of Odysseus’ journey — at least in war, he knew his enemies. Enemies during peacetime wear many masks; Odysseus must do the same if he is to survive.
Composition and Structure
Like the Iliad, Homer’s second epic is culled from legends and folktales in the oral tradition before Homer. The Odyssey was composed around 750-700 bce, during the Greek Dark Ages, a time when writing was not yet widespread, and stories were passed down orally through the generations. Homer codified these stories into a structural whole using an objective, realistic, and unromantic style. It is the second of Homer’s two great epic poems, the first being the Iliad, the story of Achilles rage and the Trojan War. The Odyssey consists of 24 books, written in dactylic hexameter, the traditional meter of epic poetry. The poem is divided into three main sections: the Telemachiad, which follows the journey of Odysseus’ son Telemachus as he searches for his father; the Wanderings, which tells the story of Odysseus’ long journey home; and the Homecoming, which describes Odysseus’ return to Ithaca and his reunion with his family.
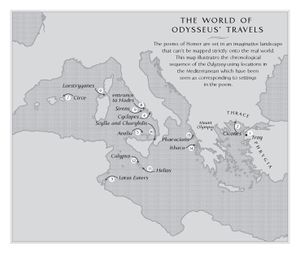
Ancient Geography
The Odyssey takes place in ancient Greece, with most of the action occurring on the Mediterranean Sea and the surrounding islands—the scope of the known world at the time. Odysseus’ journey takes him to many exotic locations, including the island of the Cyclops, the land of the Lotus-eaters, and the underworld of Hades. Along the way, he encounters a diverse cast of characters, including gods, monsters, and mortal men.
Themes and Motifs
The "Odyssey" is a rich tapestry of themes and motifs that explore the human experience. One of the central themes is the importance of home and family, as Odysseus longs to return to his wife Penelope and son Telemachus. Other important themes include the power of cunning and intelligence, the dangers of temptation and curiosity, and the importance of loyalty and hospitality. The poem also features a number of recurring motifs, such as the idea of disguise and deception, the concept of testing one's identity, and the symbolism of journeys and wandering.
Political Order
What sort of order does the Odyssey advocate? If Odysseus is the hero of the epic, then the order he finally returns to Ithaca should be the epitome of the order of the Greek paideia that created and maintained the stories found within the Odyssey. One of the concerns of a new civilization is the question of the nature of the political community: just what is lost in the absence of an ordering principle; what is gained in affirming these social structures?
The Odyssey portrays many social and political orders — like the Cyclops, the Laestrygonians, the Phaeacians, Circe, Calypso, etc. — vis-à-vis that of Odysseus’ hierarchical and patriarchal order in Ithaca. Odysseus’ Ithaca seems to represent the cultural preferences of this time in presenting values of hospitality, faithfulness, narrative, ritual, intelligence, and others as those most likely to benefit the culture. While the Iliad emphasized traits necessary for war and destruction, the Odyssey is concerned building and maintaining a political order for the good of the individual and family.
While maintaining and advocating a certain political and social order, that order represented in the Odyssey is certainly not above criticism, especially from those of us looking back at their culture in an attempt to see how it influenced our own, like attitudes toward women, hospitality, religion, violence, and war.
Characters
The Odyssey is not only an epic journey but also a study of human nature. The characters in this timeless work are complex and multifaceted, each with their own strengths, flaws, and motivations. From the cunning and resourceful Odysseus to the loyal and patient Penelope, the characters in the Odyssey have captured the imagination of readers for thousands of years.
Odysseus, whose name means “a curse’s victim or an avenger who carries a curse to others,”[1] is certainly not without his own weaknesses. He is probably best known as the wily Odysseus: as Achilles was the strongest warrior, Odysseus is the smartest. While he is “skilled in all ways of contending” (both polytropos, or “versatile,” and polymetis, or “with many wiles”)[2] he is still “harried for years on end” because of his pride and arrogance. He is unsuccessful in controlling his men, and deceives others any chance he gets making him the archetypal trickster. He uses disguises throughout the epic, and whenever he does use his own name, he or those he tells usually end up suffering for his honesty. He is a ladies’ man, versed as well it seems, in the ways of love; fidelity is obviously just a virtue of women in the Odyssey. Odysseus is a survivor. He is dedicated to life and living it to the full, which also has earned him the title of the archetypal adventurer. Yet despite his flaws, Odysseus does grow as a person and hero though the course of the epic, yet his growth costs him and those who are near to him much pain and difficulty.
While Odysseus is an interesting figure, the women characters in the Odyssey might be equally important even if they serve as foils to Odysseus in a patriarchal system. The women have a certain place in the order presented in the epics, and many seem docile and obedient while others are rebellious and evil. However, while they may seem that way, most are practice a subtlety that the warrior men do not grasp and even misunderstand.
While Penelope’s highest virtue is seen as her fidelity, she is very much like her husband: a wily and wary tactician. She is faithful to Odysseus, but she is also very politically shrewd and calculating in her actions. While certainly no Helen or Clytemnestra, Penelope does have characteristics of both of those women, yet is upheld as the quintessential wife of a hero.
Narrative
The Odyssey places narrative and poetry in the center of the culture. In an oral society, the rhapsode represents the center of learning and entertainment, or paideia.[3] The songs of the poets teach the customs and address the concerns of the people, wielding the stories and myths that represent the truths of Odysseus’ time as well as providing the foundation of thought in subsequent generations. Like now, the beliefs of the people must be translated into narrative — fantastic stories that highlight the values and identity of the people within the epic and those who listen to it in the future. These stories become sacred, the pith of culture that only the gods — in this case the Muse Calliope — can guarantee the authenticity of the poets’ memory. Thus, each epic begins with the invocation to the Muse in order that the story is represented in a truthful and accurate way. Odysseus pays the proper homage to the poet in book nine as he sends the blind rhapsode — perhaps a representation of the blind Homer himself[4] — a piece of meat from his own plate:
| “ | Demodokos, accept my utmost praise. |
” |
Odysseus, in the company of the Phaeacians, is about to deliver his own account of his wanderings, so rhetorically his praise of the poet makes sense. Yet, here we see the respect that Odysseus and his people held for the poet as the fount of knowledge from heaven, a storehouse of knowledge that had to do until the invention of writing superseded the importance of the poet in the culture.
The Odyssey is just such a work. It provides the myths that have formed the foundation of western civilization for over two-thousand years. While much of its contents might seem odd to us reading it today, many of the stories remain a very vibrant part of not only our past, but also our present, for better or worse. In knowing the stories from our history, we can know ourselves a bit better and let the wanderings of Odysseus delight us as well as teach us about many of our beliefs and cultural traditions.
Legacy
The Odyssey has had a profound influence on Western literature and culture, inspiring countless works of art, literature, and film. Its impact can be seen in everything from James Joyce's Ulysses to the Coen Brothers’ film O Brother, Where Art Thou? The poem has also played an important role in shaping our understanding of ancient Greece, providing a glimpse into the beliefs, values, and customs of this fascinating culture. Even today, the Odyssey continues to captivate readers and scholars alike with its timeless themes and vivid storytelling.
Citations
- ↑ Bloom 2007, p. 7.
- ↑ Hexter 1993, p. 4.
- ↑ Hexter 1993, p. xxix.
- ↑ Hexter 1993, p. 105.
Works Cited
- Bloom, Harold (2007). Homer’s The Odyssey. Bloom’s Guides. New York: Chelsea House.
- Hexter, Ralph (1993). A Guide to the Odyssey. New York: Vintage. p. 4.